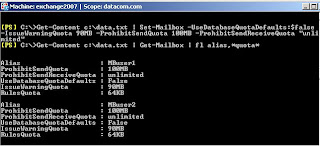
Por server:
Get-MailboxDatabase -server NOMBRE_DEL_SERVER | Select Server, StorageGroupName, Name, @{Name="Size (GB)";Expression={$objitem = (Get-MailboxDatabase $_.Identity); $path = "`\`\" + $objitem.server + "`\" + $objItem.EdbFilePath.DriveName.Remove(1).ToString() + "$"+ $objItem.EdbFilePath.PathName.Remove(0,2); $size = ((Get-ChildItem $path).length)/1048576KB; [math]::round($size, 2)}}, @{Name="Size (MB)";Expression={$objitem = (Get-MailboxDatabase $_.Identity); $path = "`\`\" + $objitem.server + "`\" + $objItem.EdbFilePath.DriveName.Remove(1).ToString() + "$"+ $objItem.EdbFilePath.PathName.Remove(0,2); $size = ((Get-ChildItem $path).length)/1024KB; [math]::round($size, 2)}}, @{Name="No. Of Mbx";expression={(Get-Mailbox -Database $_.Identity | Measure-Object).Count}} | Format-table -AutoSize

Por base de datos:
Get-MailboxDatabase -identity NOMBRE_DE_base | Select Server, StorageGroupName, Name, @{Name="Size (GB)";Expression={$objitem = (Get-MailboxDatabase $_.Identity); $path = "`\`\" + $objitem.server + "`\" + $objItem.EdbFilePath.DriveName.Remove(1).ToString() + "$"+ $objItem.EdbFilePath.PathName.Remove(0,2); $size = ((Get-ChildItem $path).length)/1048576KB; [math]::round($size, 2)}}, @{Name="Size (MB)";Expression={$objitem = (Get-MailboxDatabase $_.Identity); $path = "`\`\" + $objitem.server + "`\" + $objItem.EdbFilePath.DriveName.Remove(1).ToString() + "$"+ $objItem.EdbFilePath.PathName.Remove(0,2); $size = ((Get-ChildItem $path).length)/1024KB; [math]::round($size, 2)}}, @{Name="No. Of Mbx";expression={(Get-Mailbox -Database $_.Identity | Measure-Object).Count}} | Format-table -AutoSize